Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4) batteries have become increasingly popular in recent years due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and improved safety features. One of the key advantages of LiFePO4 batteries is their voltage stability, which makes them a reliable power source for various applications. Understanding the LiFePO4 voltage chart is essential for monitoring the battery’s performance and ensuring safe operation.
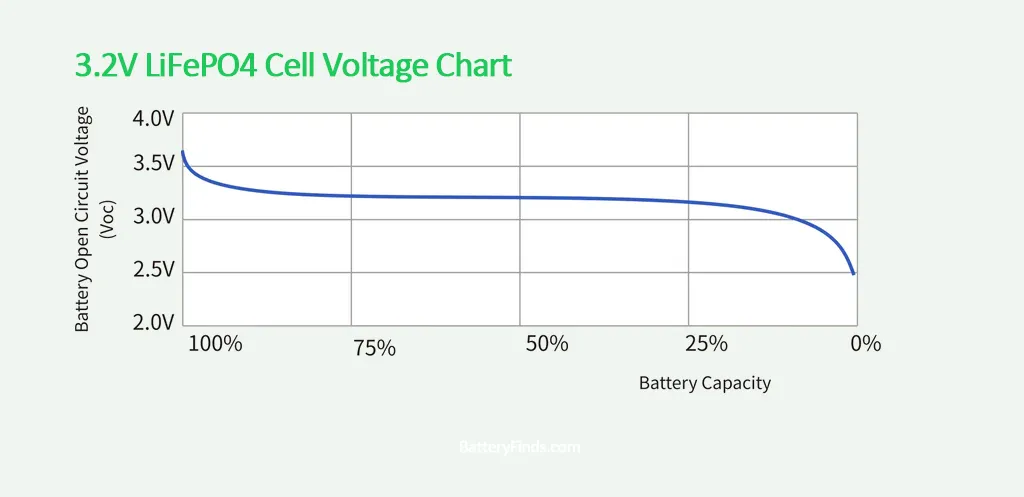
A LiFePO4 battery’s voltage varies depending on its state of charge. The voltage rises as the battery charges and falls as it discharges. The relationship between voltage and state of charge is non-linear, meaning that a small change in voltage can cause a significant change in State of Charge (SOC).
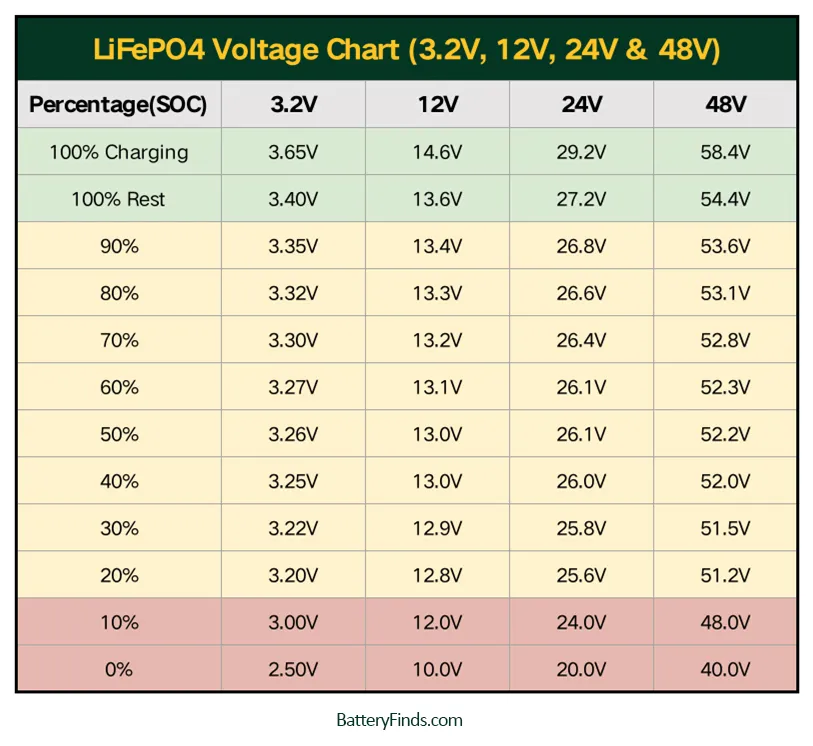
The following table shows the typical voltage ranges for a LiFePO4 battery at different states of charge:
Effects of Voltage on LiFePO4 Battery Performance
Capacity
The battery capacity is directly proportional to its voltage. As the voltage increases, the battery’s capacity also increases. For instance, a 12V LiFePO4 battery will have a higher capacity than a 6V battery of the same size. Therefore, it is crucial to choose the right voltage rating based on the project’s power requirements.
Charging
LiFePO4 batteries require a specific charging voltage and current for optimal performance. If the charging voltage is too low, the battery will not charge fully, and its capacity will be reduced. On the other hand, if the charging voltage is too high, it can lead to overcharging, which can damage the battery and reduce its lifespan. Therefore, it is essential to use a charger that matches the battery’s specifications to ensure safe and efficient charging.
You can also read more: LiFePO4 Battery Charging Guide
Discharging
The battery’s discharge voltage also affects its performance. If the battery is discharged below the recommended voltage level, it can cause irreversible damage to the battery, reducing its capacity and lifespan. Therefore, it is essential to monitor the battery’s voltage during discharge and stop using it once the voltage drops below the recommended level.
Efficiency
The battery’s efficiency is directly related to its voltage. A higher voltage battery will be more efficient in providing power to the device. Therefore, choosing a higher voltage LiFePO4 battery for your project can increase the overall efficiency and reduce power loss.
Lifespan
The battery voltage also affects its lifespan. A higher-voltage battery may have a longer lifespan than a lower-voltage battery because it can handle more charge cycles. However, this also depends on other factors such as the quality of the battery, charging and discharging parameters, and the operating conditions.
Bulk, Float, And Equalize Voltages of LiFePO4
|
Types
|
3.2V
|
12V
|
24V
|
48V
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Bulk
|
3.65V
|
14.6V
|
29.2V
|
58.4V
|
|
Float
|
3.375V
|
13.5V
|
27.0V
|
54.0V
|
|
Equalize
|
3.65V
|
14.6V
|
29.2V
|
58.4V
|
LiFePO4 Battery Charging Parameters
|
Characteristics
|
3.2V
|
12V
|
24V
|
48V
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Charging Voltage
|
3.5~3.65V
|
14.2~14.6V
|
28.4V~29.2V
|
56.8V~58.4V
|
|
Float Voltage
|
3.2V
|
13.6V
|
27.2V
|
54.4V
|
|
Maximum Voltage
|
3.65V
|
14.6V
|
29.2V
|
58.4V
|
|
Minimum Voltage
|
2.5V
|
10V
|
20V
|
40V
|
|
Nominal Voltage
|
3.2V
|
12V/12.8V
|
24V/25.6V
|
48V/51.2V
|
In conclusion, the voltage rating of a LiFePO4 battery plays a significant role in determining its performance and lifespan. It is crucial to choose the right voltage rating, monitor the battery’s voltage during charging and discharging, and use a suitable charger to ensure safe and efficient operation. By following these guidelines, you can maximize the battery’s performance and lifespan, and ensure reliable power for your DIY projects.

Last table is wrong the first column entry, instead of maximum voltage 4,2v should be 3,65v the rest entries looks OK
Thank you for bringing that to my attention. I apologize for the mistake in the first column entry, I have modified it to the correct data
As a thank you, we’re giving you an extra coupon, hope you’ll like it
Please check your email
For other questions or concerns, please let me know.
Best Regards
Battery Finds Team
Shouldn’t the “Minimum Voltage” in the second chart be 2.5V?
Hi Albrntt,
Thank you for your correction. The cut-off voltage of LiFePO4 discharge is 2.5V, which I have corrected. Thank you again.
Best Regards,
Eva
what if for every kind of LiFePO4 batteries (3.2V,12V,24V,48V) have voltage below their minimum voltage? can we recharge it?
Hi, Oktav
If LiFePO4 batteries of any voltage (3.2V, 12V, 24V, 48V) have dropped below their minimum voltage, it is generally not recommended to recharge them immediately. LiFePO4 batteries have a minimum voltage threshold to protect their longevity and performance. Discharging a battery below its minimum voltage can cause irreversible damage to the cells and affect their overall capacity and lifespan.
In such cases, it is advisable to take the following steps:
Disconnect the battery: Remove the battery from the device or system it is connected to.
Allow the battery to rest: Let the battery sit idle for some time (a few hours or overnight) to stabilize.
Check the voltage: Use a multimeter or battery voltage tester to measure the voltage of the battery. Ensure it has stabilized above the minimum voltage threshold for safe operation.
Recharge the battery: If the voltage has stabilized above the minimum threshold, you can proceed with recharging the battery using a compatible charger specifically designed for LiFePO4 batteries. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommended charging parameters.
It’s important to note that deep discharges and operating LiFePO4 batteries below their minimum voltage on a regular basis can significantly reduce their lifespan. Proper maintenance and monitoring of the battery’s voltage levels are crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Have any problems , just feel free to contact us
Best Regards
BatteryFinds Team
I have a Sun Solar 6.2KVA Inverter with LifePO4 48V battery and it won’t charge past 51.03v (display on battery). What could be the problem?
Hi
Thanks for your explanation.
Last month I have got a LiFePo4 24v 200A, I noticed that the battery does not reach 100% level after charging. I am monitoring the level via WatchPower mobile app that getting the data from the inverter. It used to reach 99% then after a week it becomes 98% after charging. And now it reachs 97% max. The voltage is 28.0V.
Is it normal behaviour? Or something going wrong?
Thanks in advance
When you are talking about the soc and voltage not being linear at the top you have it backwards. Voltage doesn’t drop as much compared to soc with these.
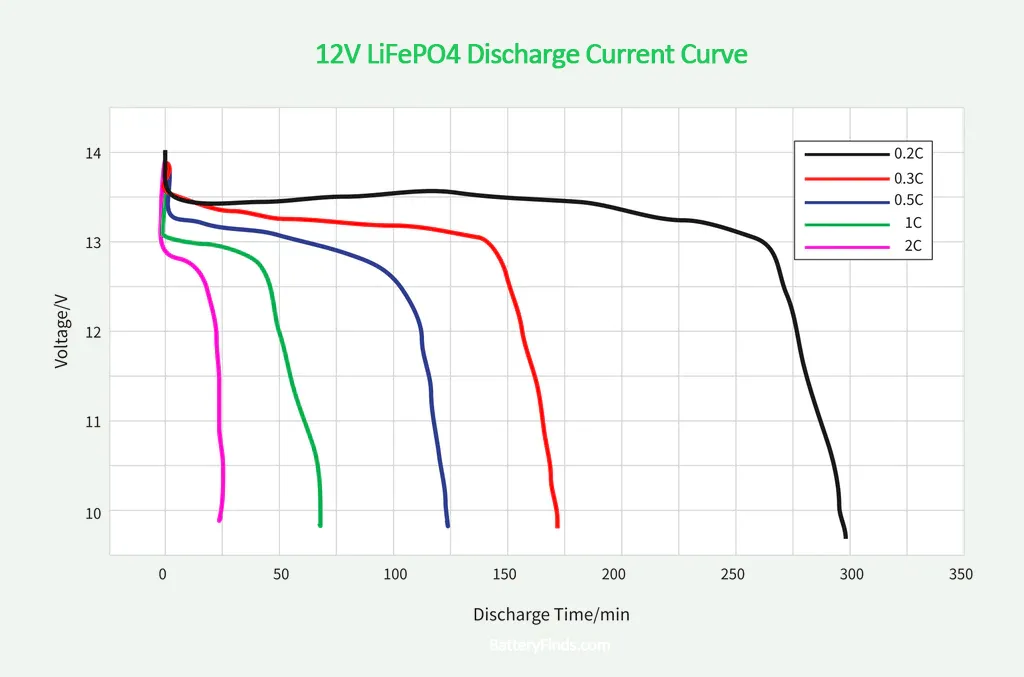
The red curve in the 12V discharge chart says “1.3C” which cannot be correct. I assume this was meant to say 0.3C.
Also, I think the words under the 3.2V Cell Voltage Chart, “meaning that a small change in SOC can cause a significant change in voltage.” is backwards and should instead say, “meaning that a small change in voltage can cause a significant change in SOC.”
Lastly, why is the first chart partially covered with a dark colored polygon that says, “Misleading Facts” ? Did someone hack your site?
Hi Dan,
Thank you for bringing these concerns to our attention. We appreciate your keen eye for detail and your engagement with our content.
You are right – the 1.3C label in the 12V discharge chart was a typo and should have read 0.3C. We apologize for the mistake and have updated the chart accordingly.
For the statement under the 3.2V Cell Voltage Chart, your understanding is spot on. The correct interpretation should be, “meaning that a small change in voltage can cause a significant change in State of Charge (SOC).” This is an important clarification, and we will revise the wording to reflect this accurately.
As for the dark-colored polygon labeled “Misleading Facts,” this is certainly not intentional and does not align with our commitment to providing clear and accurate information. It appears to be an issue with the cover design and has since been updated. We apologize for any inconvenience this may have caused and appreciate your understanding as we strive to maintain the highest standards of accuracy and clarity in our informational resources.
If you have any further questions, concerns, or feedback, please do not hesitate to reach out. Your input is invaluable in helping us improve.
Best regards,
Eva